For Low Altitude Business Strategy, Market Analysis, New Business Development, let’s meet the Daydream Team in Europe, USA, Asia
Fabrice Lacombe (fabrice.lacombe@daydream.eu), Stephanie Lorini (stephanie.lorini@dynovel.com) or Yusi Chen (yusi.chen@daydream.eu) would be pleased to meet with you.
Table of content
1. Low Altitude Economy Shanghai Expo context
2. Low Altitude Economy: a growing market with a complicated value chain
3. Upstream Materials
4. Midstream assembly & manufacturing
5. Downstream and end-user applications
6. Other players on the Value Chain
7. Future development of the LAE industry: battery is key
1. Low Altitude Economy Shanghai Expo context
The inaugural International Low-Altitude Economy (LAE) Expo, also known as the Advanced Air Mobility Expo Shanghai, themed “Empowering the Low-Altitude Economy, Empowering Thousands of Industries,” focused on the development needs of low-altitude enterprises and the implementation of application scenarios was held in July 2025.
The expo featured themed sections on low-altitude: infrastructure, manufacturing and supporting facilities, transportation, urban and rural management, commercial applications, and consumer entertainment.
Spanning 60,000 square meters, the expo featured nearly 300 exhibitors, over 30 forums and events, and attracted more than 50,000 visitors.
Daydream has issued in 2024 a D-news with more technical and market information.
https://www.daydream.eu/low-altitude-economy-opportunities-chemical-material-market/

2. Low Altitude Economy: a growing market with a complicated value chain
The low-altitude economy is heating up – this emerging sector has captured the attention of players across the entire value chain as the next frontier of growth.
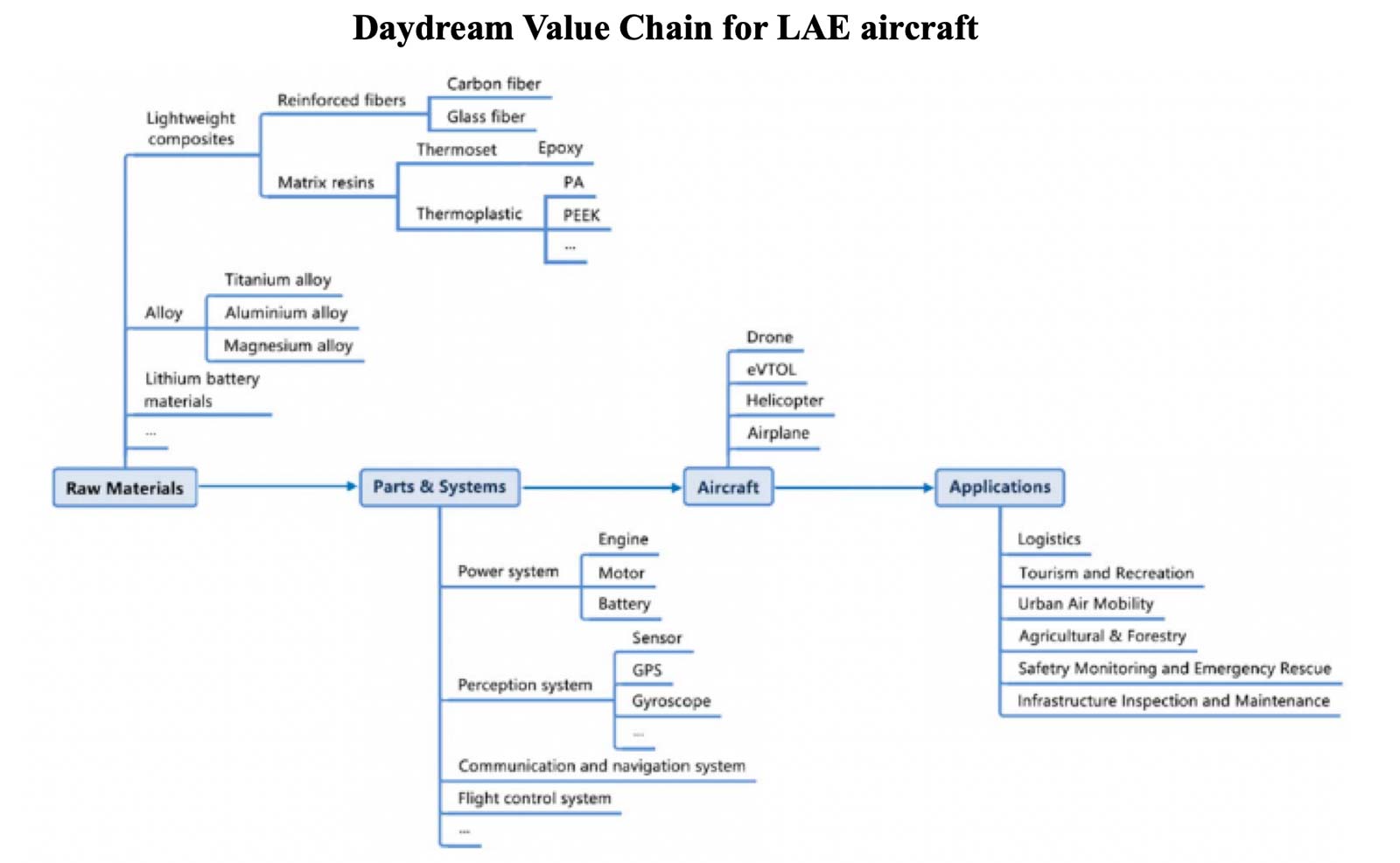
More details: https://www.daydream.eu/low-altitude-economy-opportunities-chemical-material-market/)
In the following chapters we offer some observations concerning the Value Chain and in particular the upstream, midstream and downstream representation at the Expo.
3. Upstream Materials
- Lightweight composites: Typically reinforced by carbon fiber or fiberglass with high-performance plastics and engineering plastics.
- Drone shells, blades, and frameworks made by 3D weaving carbon fiber or hot-pressing carbon fiber composites
- Engine parts made by high-performance polymer composites for their lighter weight and good heat dissipation capability.
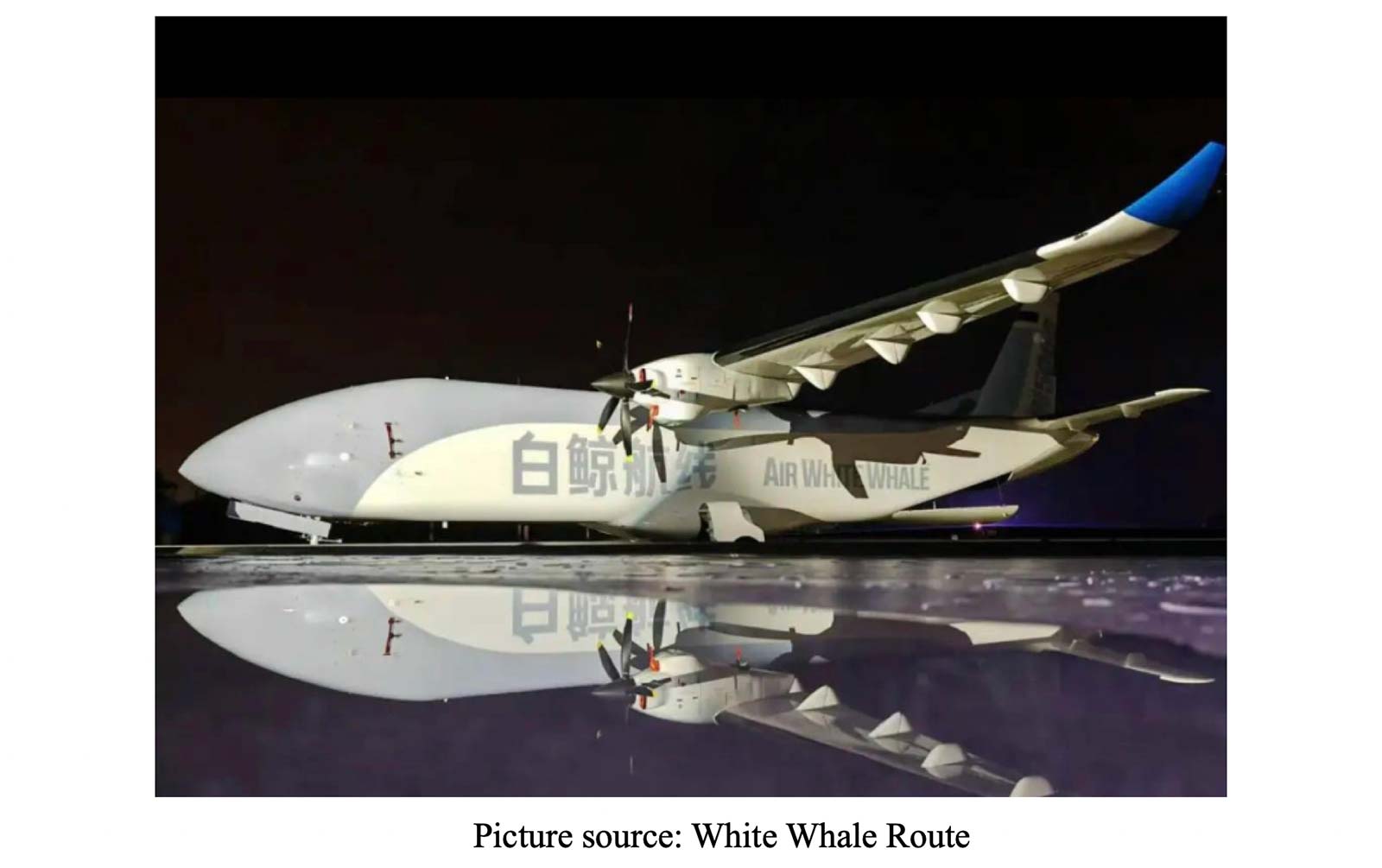
According to Low-altitude Economy 100, the W5000 ‘White Whale Route’ UAV demonstrates China’s aerospace advancements: a 40% weight reduction through indigenous carbon fiber composites enables 5-ton payload delivery over 800km, achieving 2.7 RMB/ton-km operational efficiency.

- Lightweight composites suppliers: More local players attended the exhibition, while Avient is the only identified foreign raw material supplier with a booth there.


4. Midstream assembly & manufacturing
- Chinese local companies, especially state-owned enterprises, dominate the assembly of complete drones, focusing on high-liability designs.
- Some local non-state-owned companies in the exhibition:
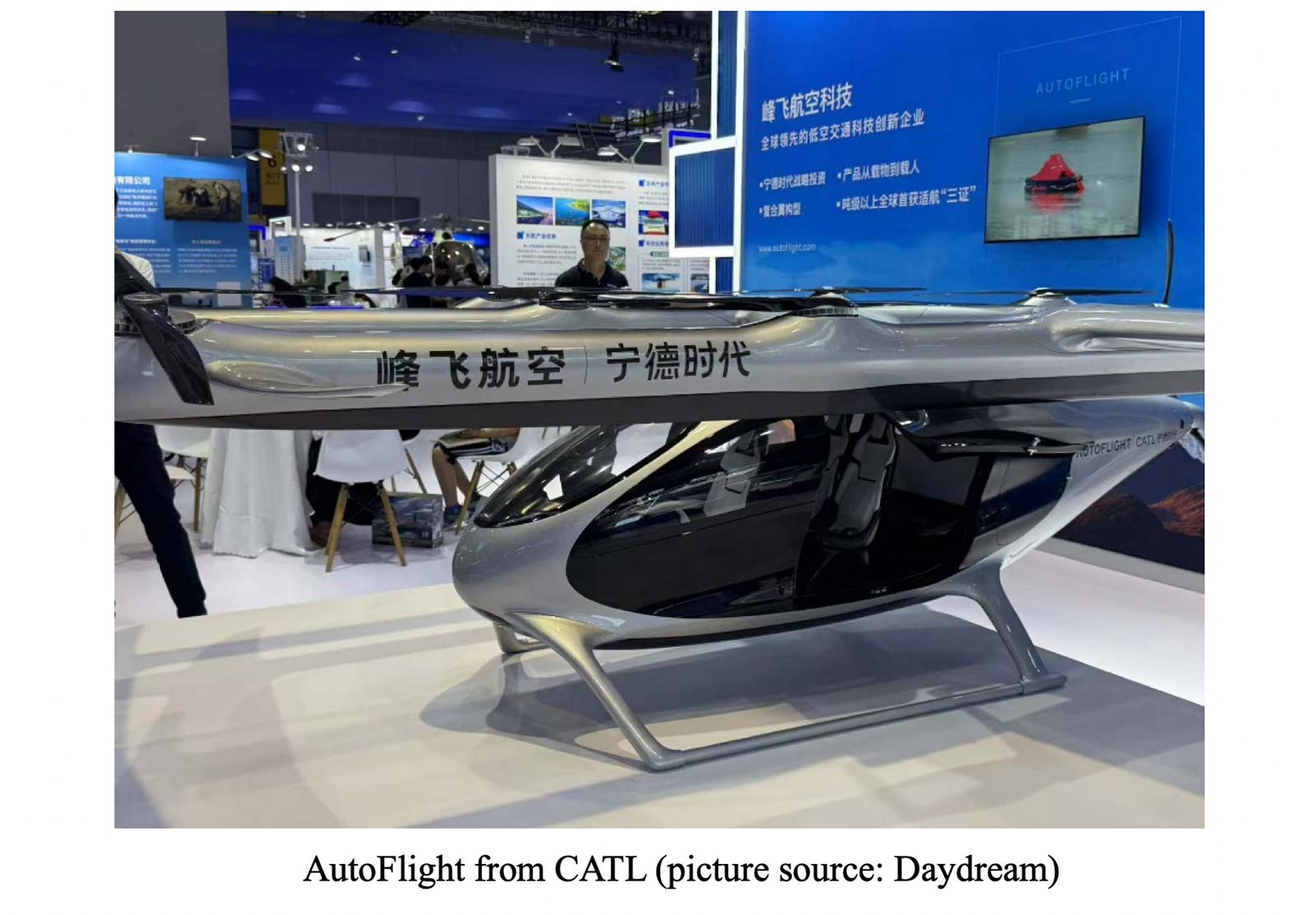
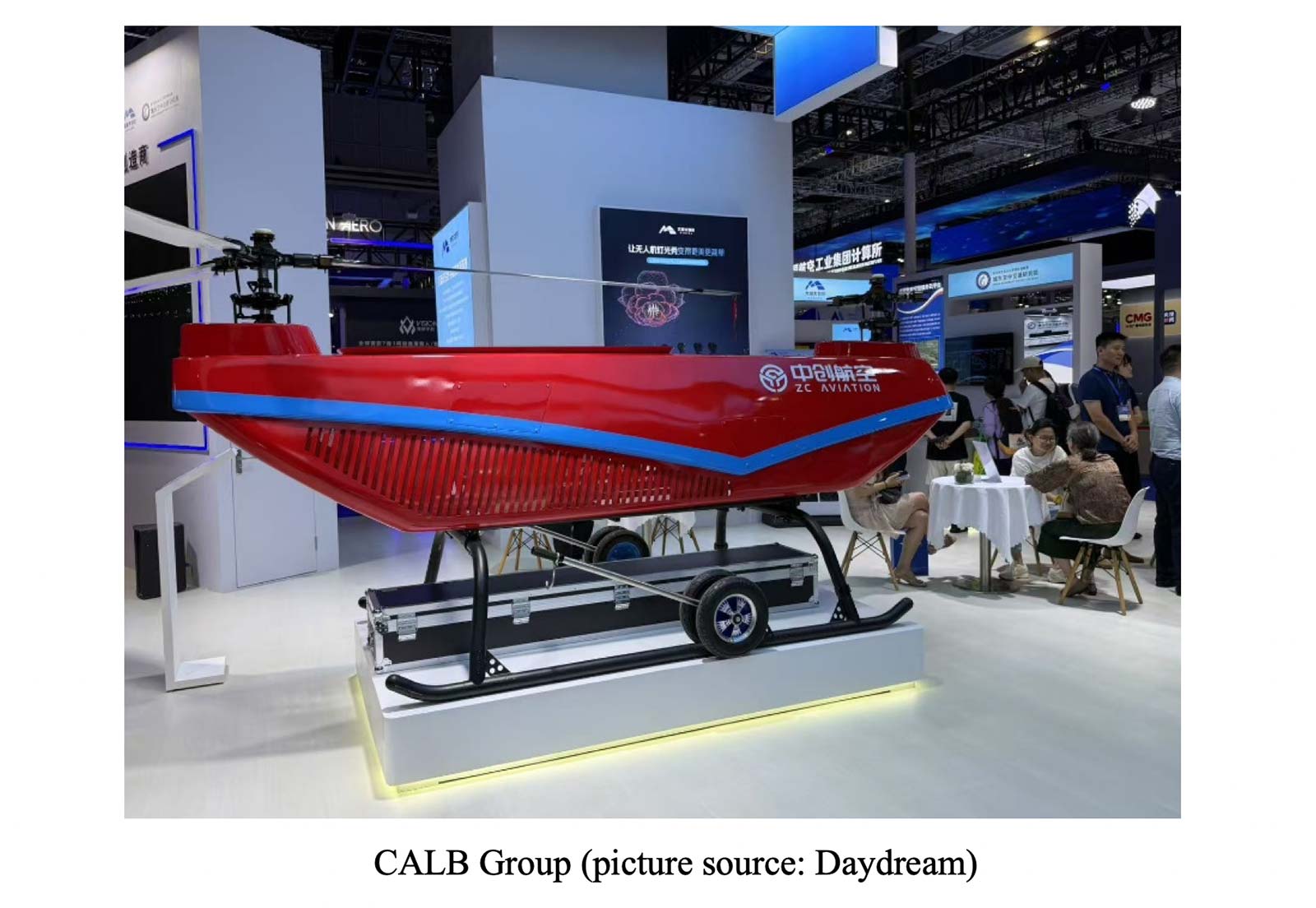


- Some foreign-invested or foreign companies in the exhibition:
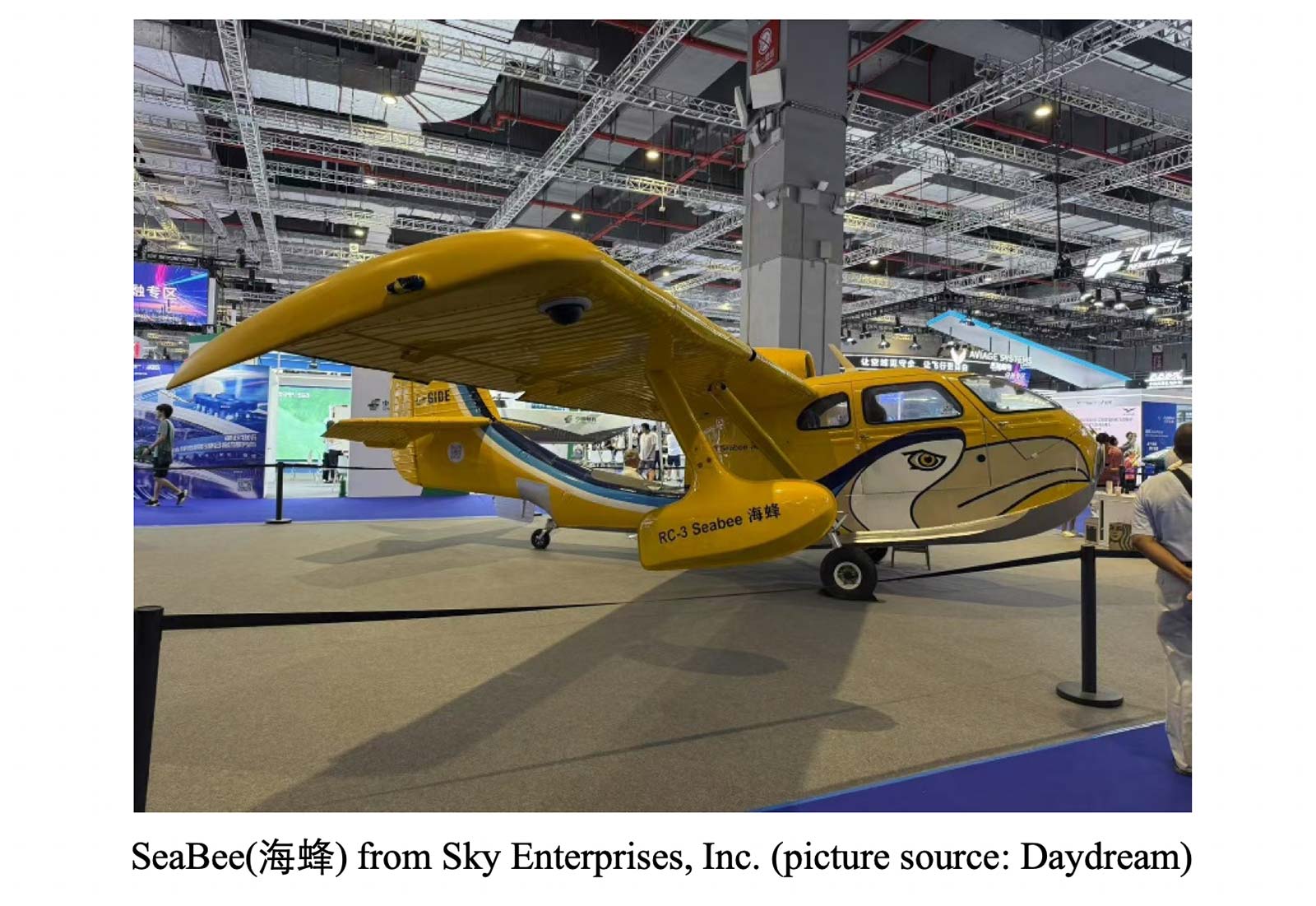

5. Downstream and end-user applications
- Transportation of cargo before passengers: Most companies are prioritizing cargo delivery trials, with passenger transportation expected to emerge in the next 3–5 years.
- Key end-user segments with more mature applications:
- Crop protection (spraying pesticides, seeding fields)
- Example, DJI Agriculture, a global leader, operates drones covering one-third of China’s farmland, with applications ranging from rice paddies to fruit orchards.
- Crop protection (spraying pesticides, seeding fields)
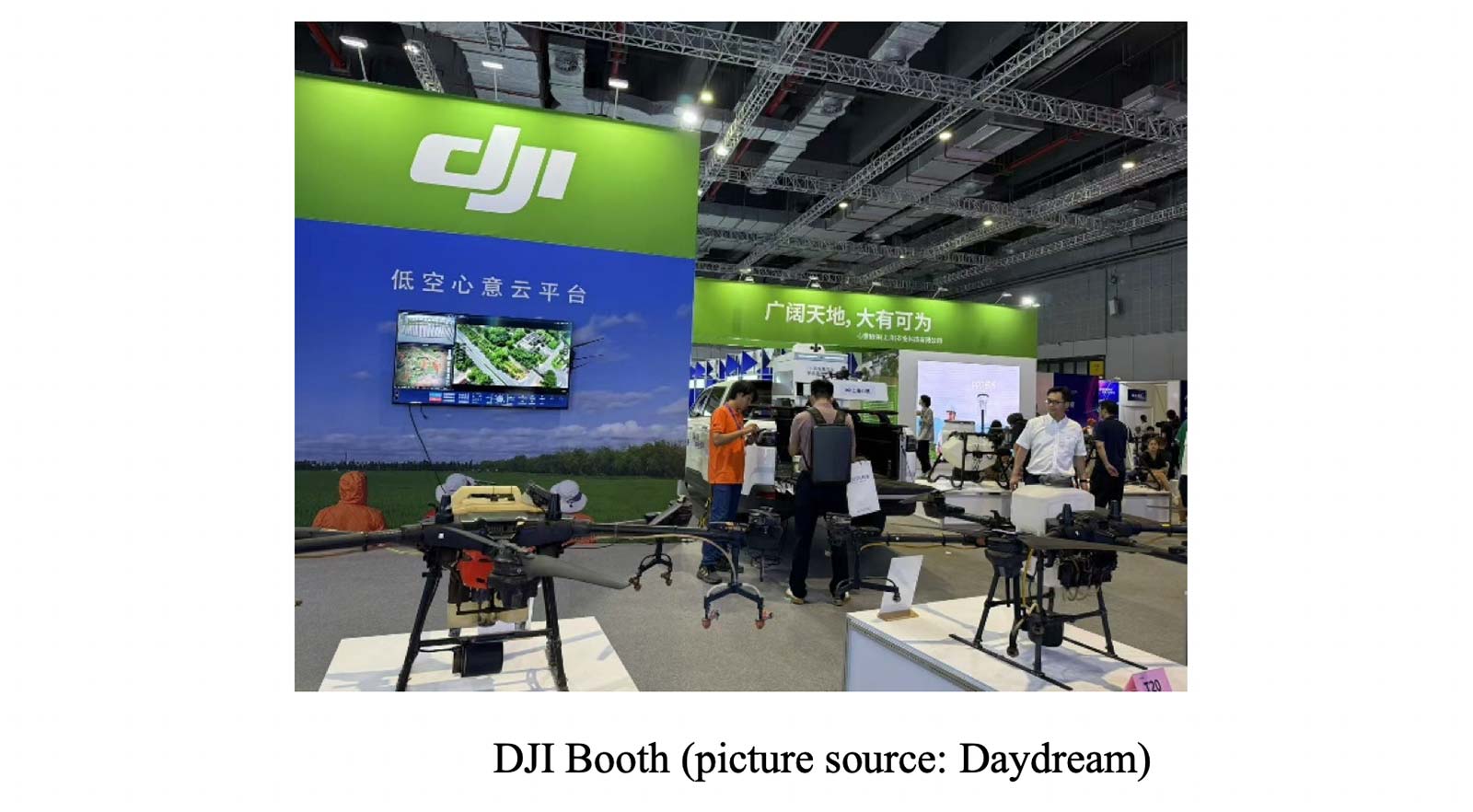

-
- Firefighting & emergency response
- Weather monitoring
- High-altitude work (lifting heavy loads, cleaning skyscraper facades)
- Short-distance delivery of high-value cargo
- Example, The Longhua Low-Altitude Economy Association is testing a Shanghai-Zhoushan-Ningbo route (~300 KM) to deliver seafood, cutting delivery time to just 30 minutes one-way.
- Drone light shows (This type of drone is a little more complicated than consumer-grade drones, because they need to work together in large numbers, so the accuracy of signals and positioning will be higher.)
6. Other players on the Value Chain
There are also other players impacting the development of this industry that attended the exhibition, including:
- Training schools for drone pilots (over 220,000 licensed operators in China)
- Government bodies, administrative agencies, and relevant organizations involved in legislation and standards development
- Technology companies, including tele-communication, image processing, anti-drone systems, etc.
7. Future development of the LAE industry: battery is key
Apart from the opportunities in this market, one significant hurdle for the low-altitude economy industry is energy supply, particularly battery technology. The current systems in use include:
- Lithium Batteries:
- Applications: consumer drones (such as camera-toting quadcopters)
- Issue: Short endurance (20-30 mins), limiting them to quick tasks like aerial photography
- Hybrid Systems (Fuel + Batteries):
- Applications: agricultural drones
- Gas engines generate power for electric motors, balancing payload capacity and flight time – ideal for spraying large farms throughout the day.
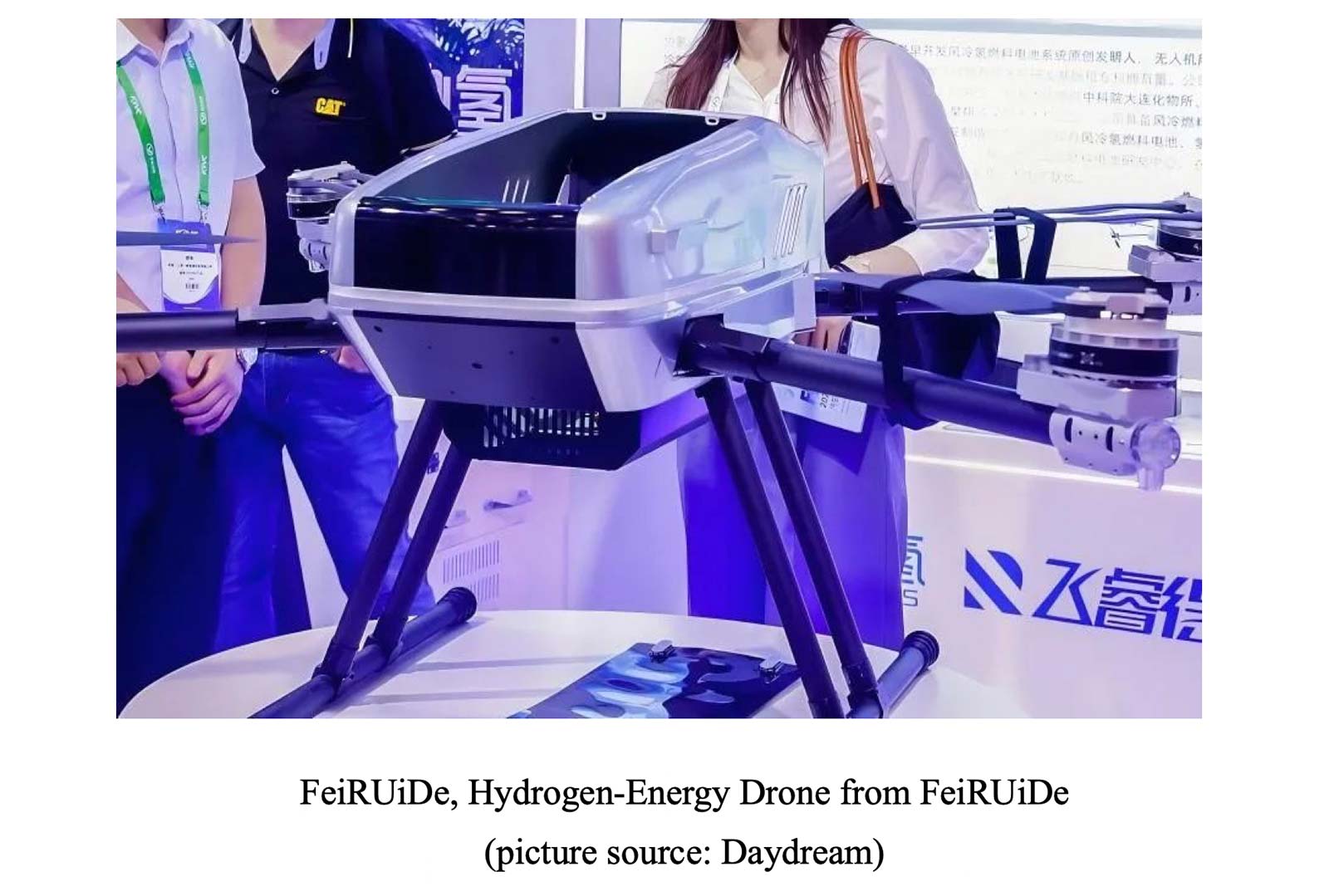
- Hydrogen Energy / Fuel cell:
- Application: medical assistance, forest firefighting
- Benefits: Longest endurance (2-3 hours) and zero emissions
- According to the Fuel Station Industry Development Research Institute, hydrogen-powered drone propulsion system comprises hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen storage tanks, delivering 3-5 times the energy density of lithium batteries. They can achieve an endurance of 3-10 hours and operate reliably across a wide temperature range from -40°C to 60°C.”











